这篇帖子我们讲一下如何用我们投研进行python参数优化,我们以下面的代码为例。
这个示例策略是指5日线上穿20日线时买入,下穿时卖出的策略。可以更改参数值,来获取不同的数据比较,最终得出最优的参数。
#encoding:gbk
#int(ma_fast_period) = 3 # 快线
#int(ma_slow_period) = 10 # 慢线
"""
5日线上穿20日线时开多,下穿时开空
"""
# ma_fast_period = 5
# ma_slow_period = 20
import time
def init(ContextInfo):
#回测参数设置
ContextInfo.start = "2015-02-10 00:00:00" # 注意格式,不要写错
ContextInfo.end = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')+ " 00:00:00" # 注意格式,不要写错
ContextInfo.set_commission(0, [0.001,0,0,0,0,0.002]) # 手续费设置为千1
ContextInfo.code = ContextInfo.stockcode + '.' + ContextInfo.market
ContextInfo.account_id = 'backtest' # 回测时随便写一个字符串当作账号,交易相关接口需要用到
ContextInfo.buyed = 0
def handlebar(ContextInfo):
timetag = ContextInfo.get_bar_timetag(ContextInfo.barpos)
bar_date = timetag_to_datetime(timetag, '%Y%m%d')
price = ContextInfo.get_market_data_ex(['close','open'],
stock_code=[ContextInfo.code],
count = int(ma_slow_period) + 2,
period= ContextInfo.period,
end_time=bar_date,
)[ContextInfo.code]
# print(bar_date, price.to_dict())
price_dict = price.to_dict('list')
close_list = price_dict['close'][:-1]
print(close_list)
# 昨日ma计算
fast_ma = sum(close_list[-1 * int(ma_fast_period): ]) / int(ma_fast_period)
slow_ma = sum(close_list[-1 * int(ma_slow_period): ]) / int(ma_slow_period)
# 前日ma计算
close_list = price_dict['close'][:-2]
fast_ma_last_bar = sum(close_list[-1 * int(ma_fast_period): ]) / int(ma_fast_period)
slow_ma_last_bar = sum(close_list[-1 * int(ma_slow_period): ]) / int(ma_slow_period)
cross_up = fast_ma_last_bar <= slow_ma_last_bar and fast_ma > slow_ma
cross_down = fast_ma_last_bar >= slow_ma_last_bar and fast_ma < slow_ma
bar_open = price_dict['open'][-1]
if cross_up:
# 买入
passorder(23, 1123, ContextInfo.account_id, ContextInfo.code,
11,
bar_open,
0.8,
ContextInfo) # 用80%的资金开仓, 开仓价为当日开盘价
ContextInfo.draw_text(True, 0, '1')
elif cross_down:
# 卖出
ContextInfo.draw_text(True, 0, '0')
passorder(24, 1123, ContextInfo.account_id, ContextInfo.code,
11,
bar_open,
1,
ContextInfo)
def query_info(ContextInfo):
orders = get_trade_detail_data(ContextInfo.account_id, 'future', 'order')
orders = [to_dict(o) for o in orders]
deals = get_trade_detail_data(ContextInfo.account_id, 'future', 'deal')
deals = [to_dict(t) for t in deals]
positions = get_trade_detail_data(ContextInfo.account_id, 'future', 'position')
positions = [to_dict(p) for p in positions]
accounts = get_trade_detail_data(ContextInfo.account_id, 'future', 'account')
accounts = [to_dict(a) for a in accounts]
return orders, deals, positions, accounts
def to_dict(obj):
attr_dict = {}
for attr in dir(obj):
try:
if attr[:2] == 'm_':
attr_dict[attr] = getattr(obj, attr)
except:
pass
return attr_dict
这个代码里面的两个参数int(ma_fast_period)代表的是快线,int(ma_slow_period)代表是慢线。
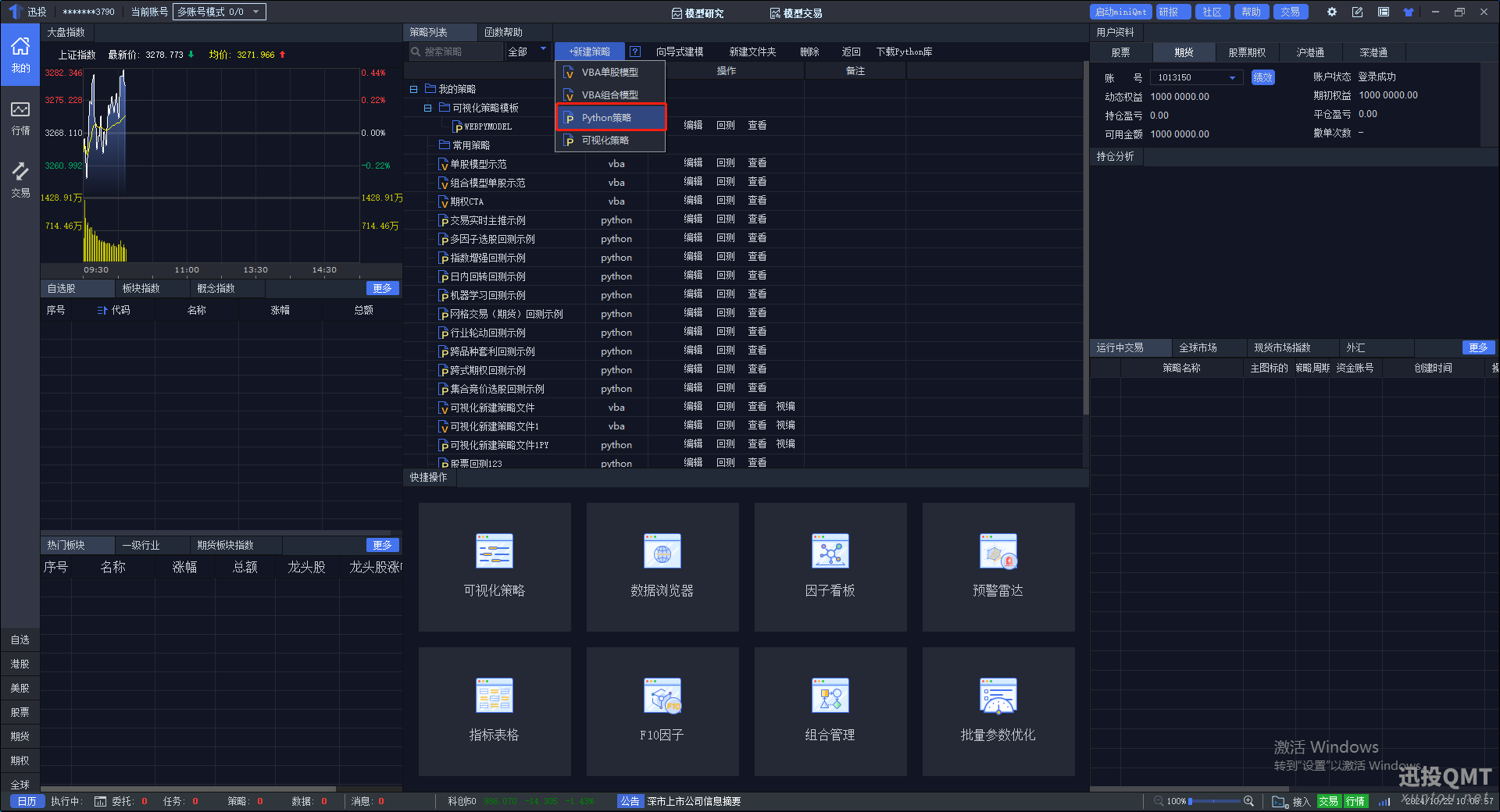
第一步:点击新建策略里面的python策略
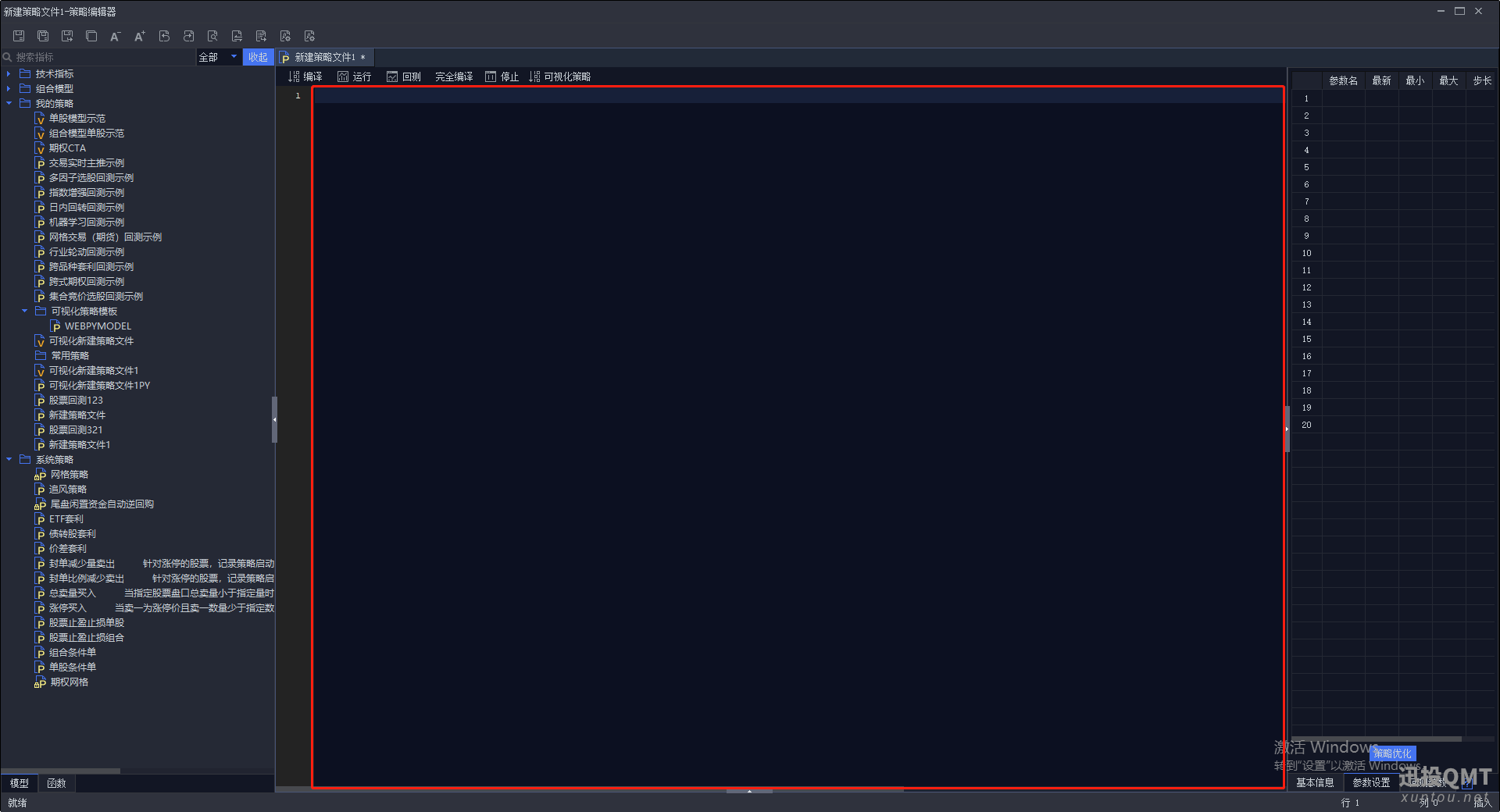
第二步:把代码复制到这个空白区域
第三步:点击右下角参数设置按钮
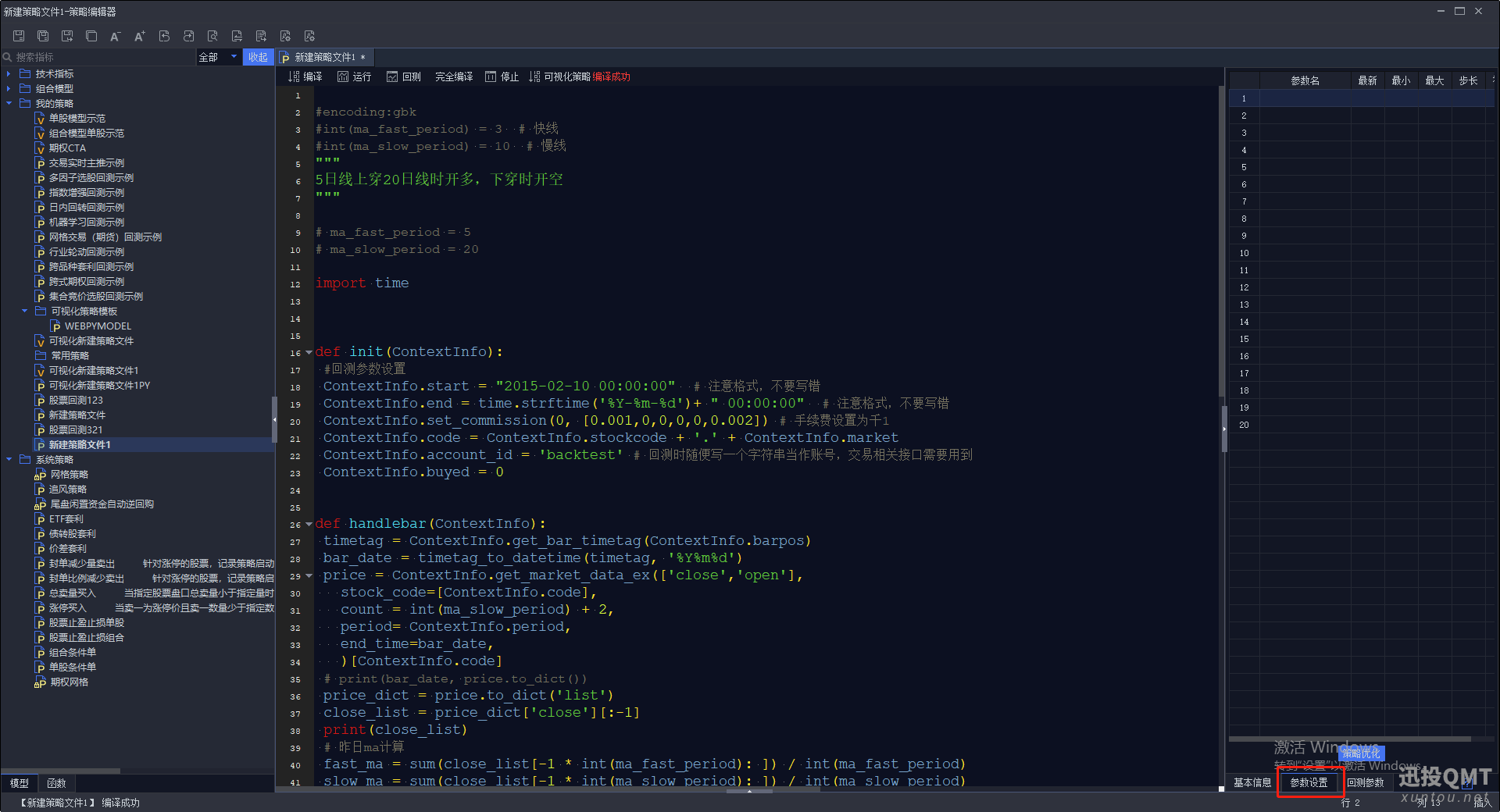
第四步:定义好自己的参数
在这个策略中参数名要设置2个,一个设置成ma_fast_period ,一个设置成ma_slow_period
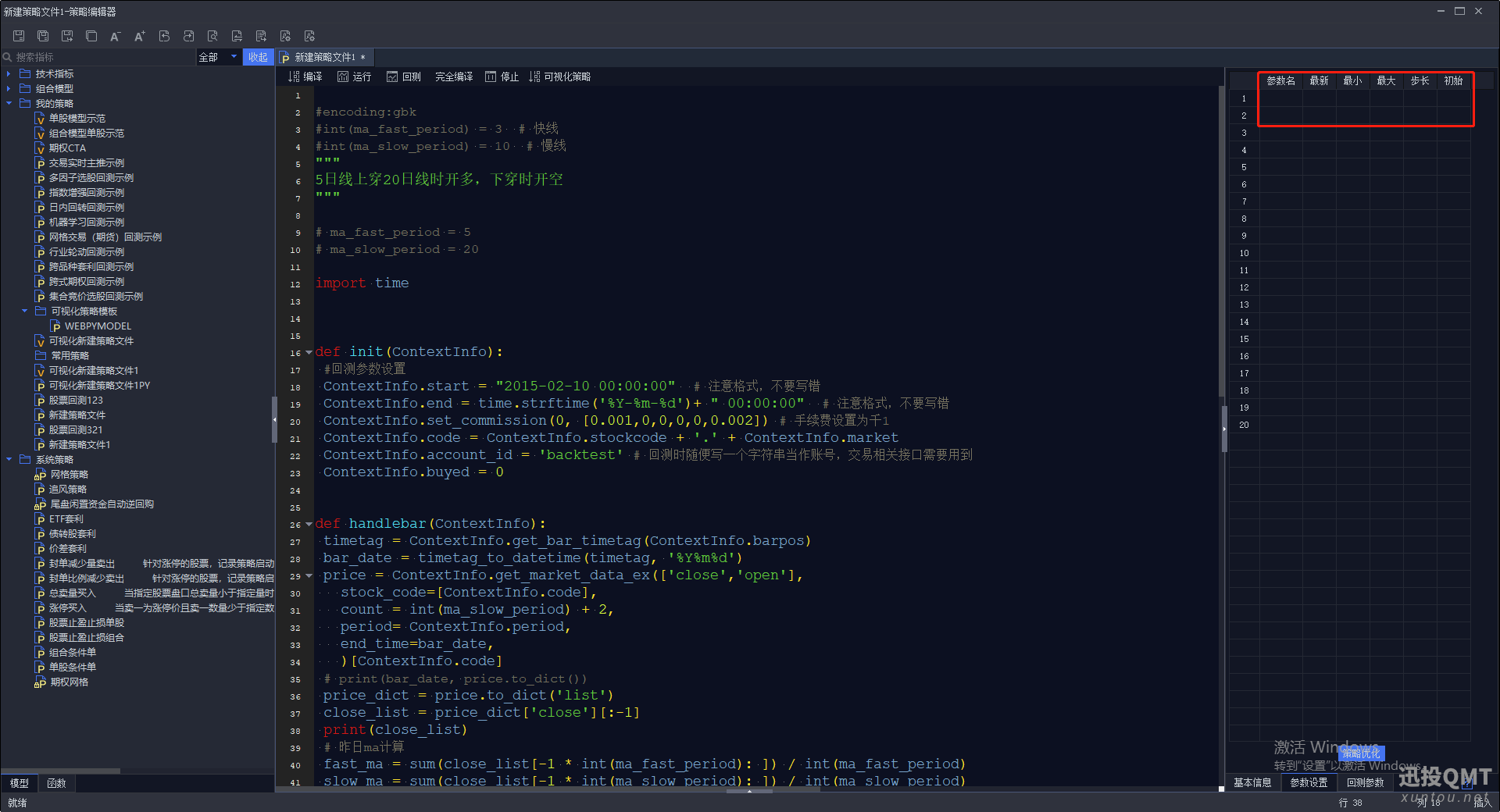
第五步:点击运行按钮
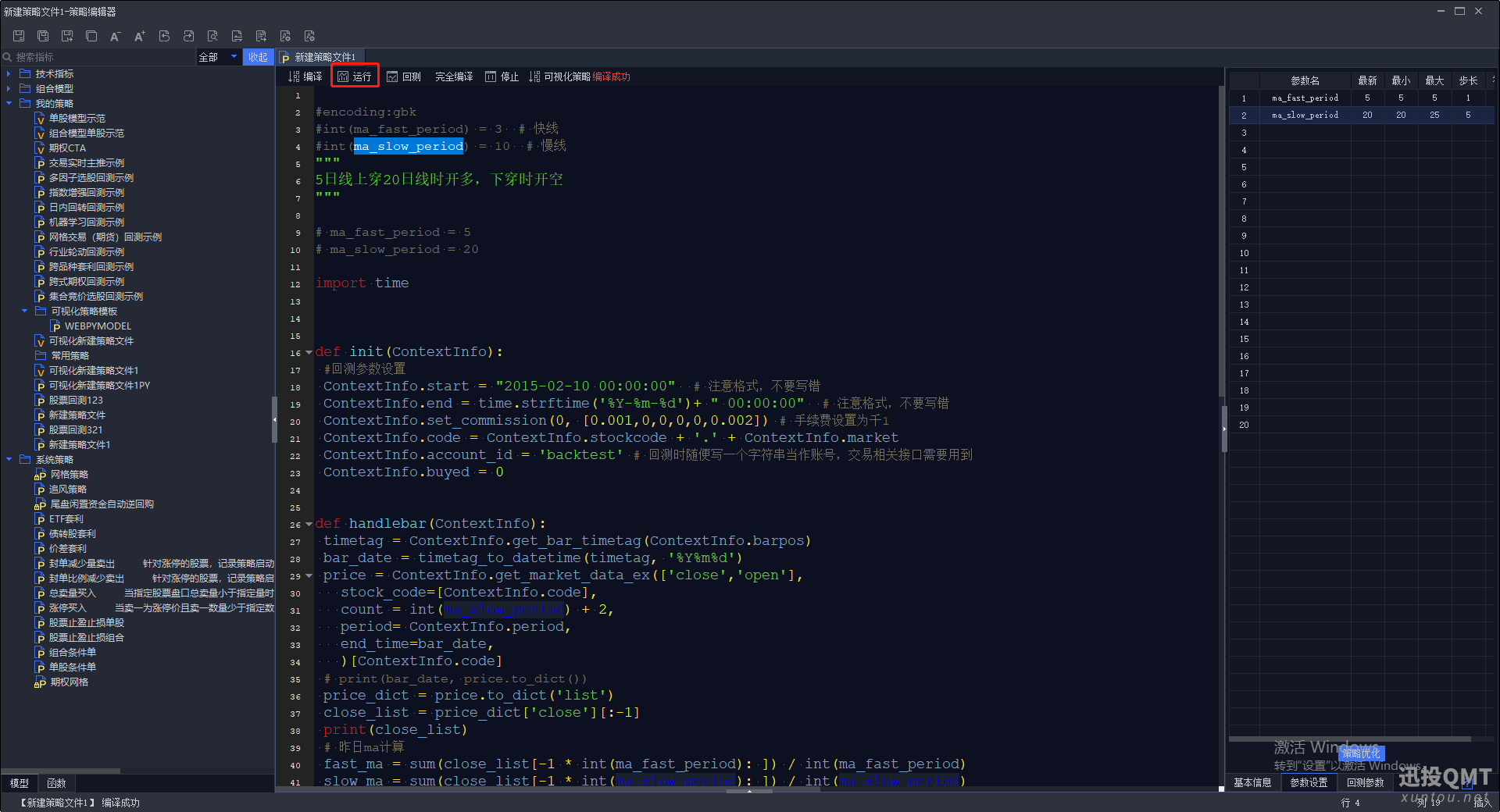
第六步:点击策略优化按钮
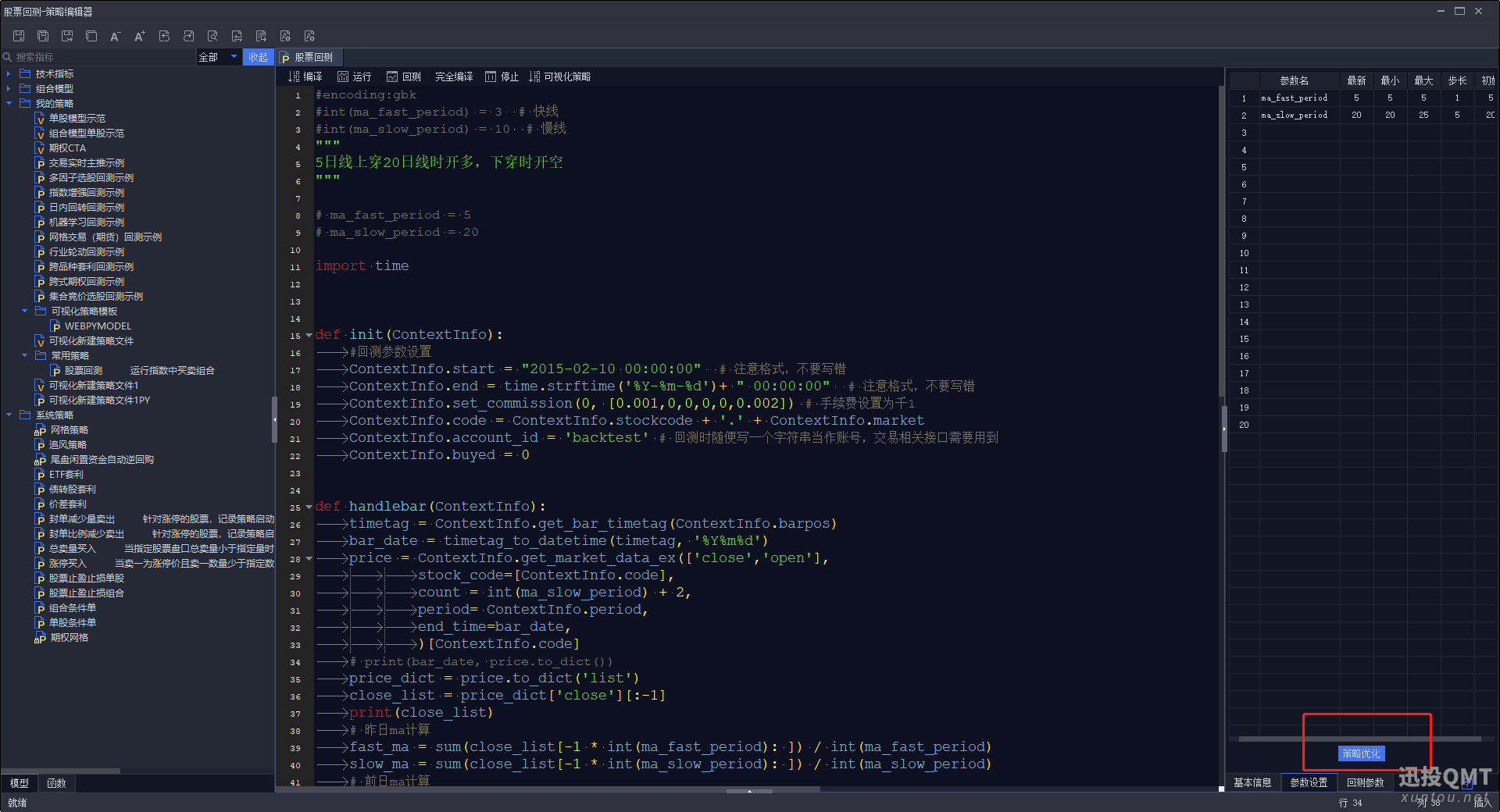
第七步:复权方式默认选择等比后复权,根据自己的情况更改,然后选择自己的品种,计算周期,然后右边可以选择自己想得到的结果。
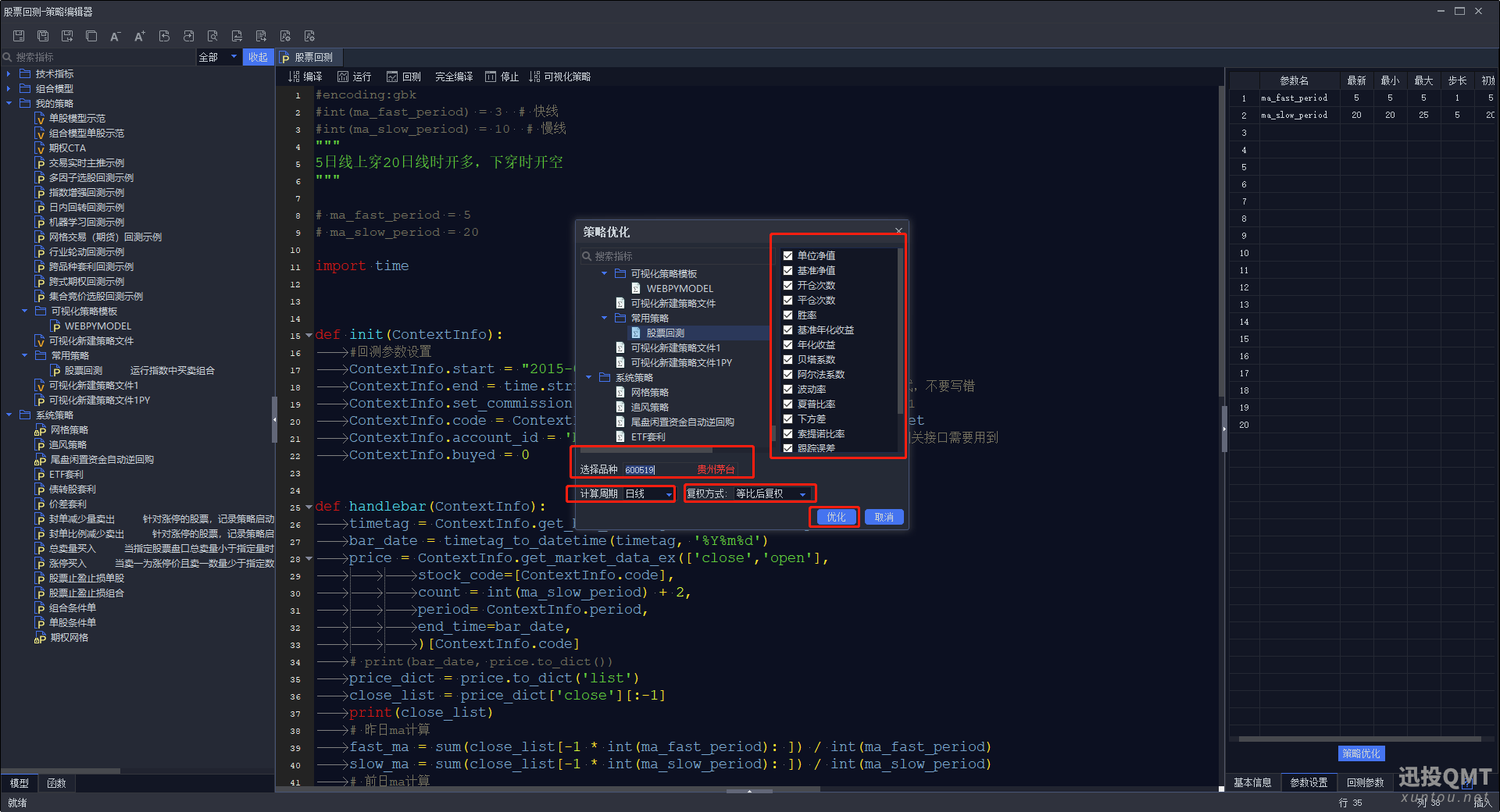
第八步:定义自己的参数,定义好点击开始
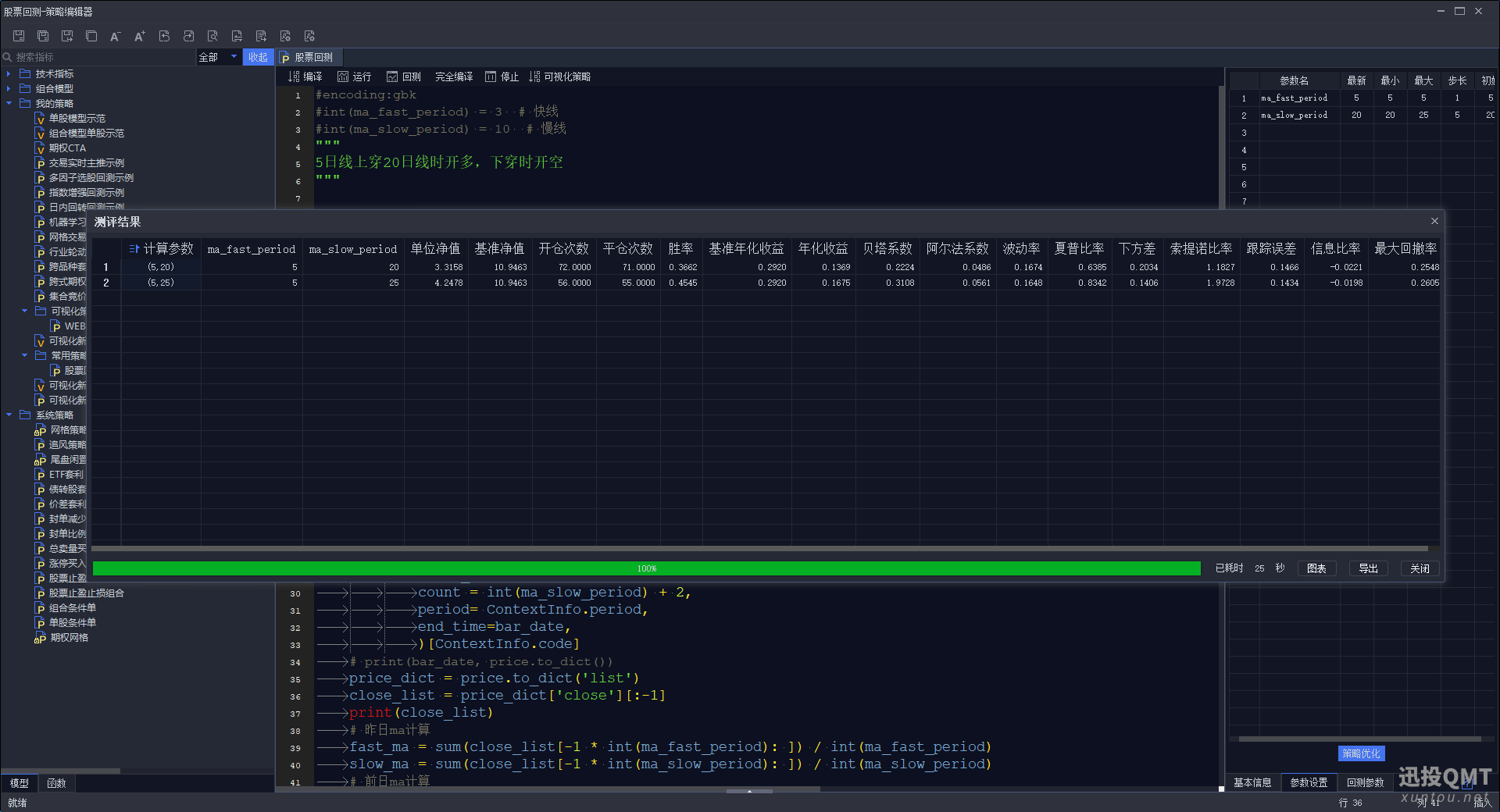
这里就相当于一个排列组合,快线是从5开始,到5结束,步长为1,一共有一种数据。慢线是从20开始,到25结束,步长为2,一共有两种数据。所以优化组合是2种。
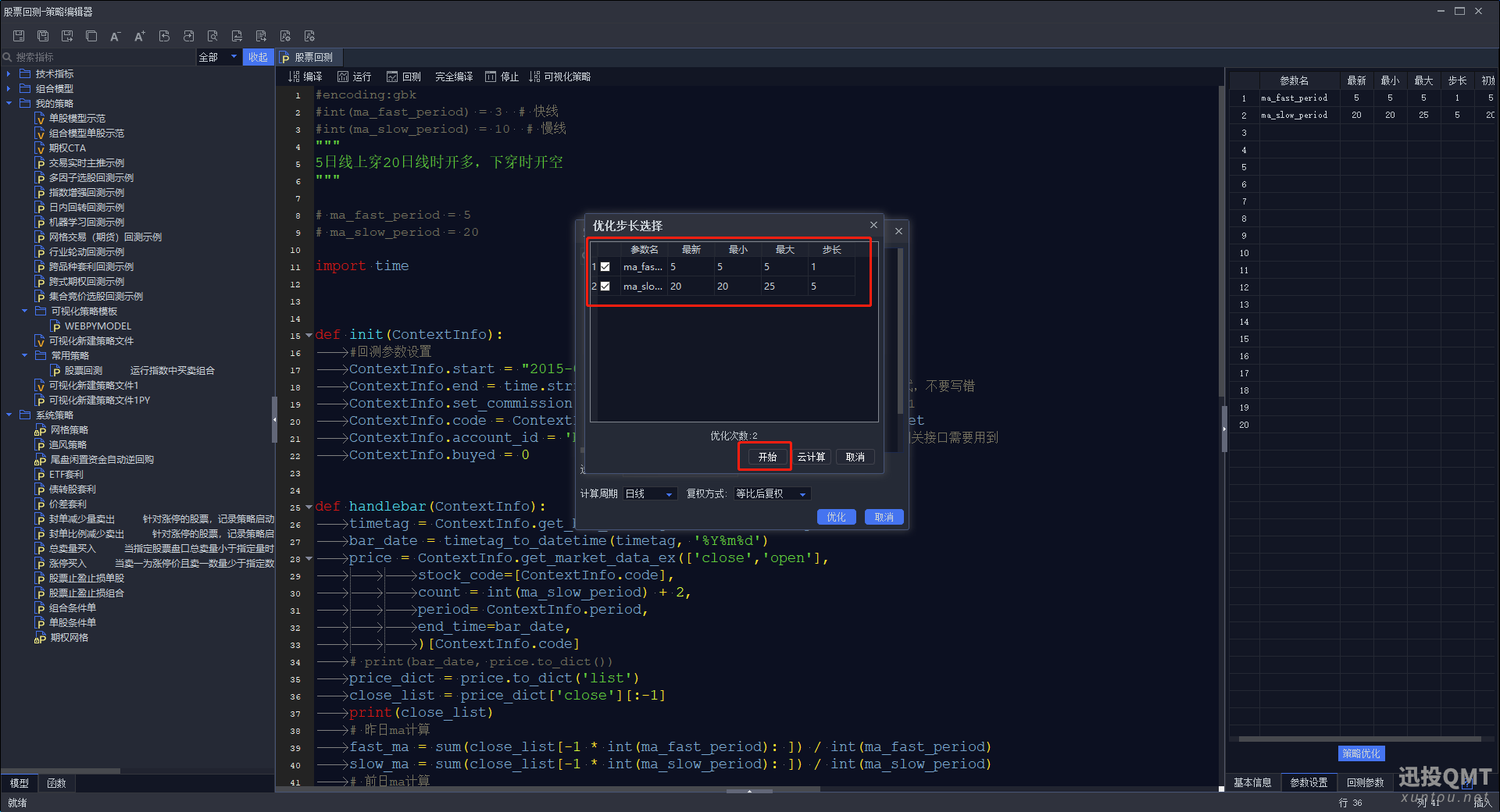
最后我们就可以根据结果来选择自己想要的参数了。